- Metabolism & Clinical Biochemistry 31 experiments
- Nutritional and Food Biochemistry 24 experiments
- Industrial Biochemistry 15 experiments
- Biochemical Techniques & Equipment 17 experiments
- Plant Biochemistry 20 experiments
- Scientific English Writing and Research Tools 14 exercises
Ordering Information
Price: 600/- PKR
Edition: 2023-2024 (1st edition)
ISBN: 978-627-7502-06-5 (Print)
This Series contains One hundred and twenty one (121) full length experiments
Published by Dr. Muhammad Ali
© Copyright 2022. All rights reserved by Dr. Muhammad Ali
Contact us for purchase and online ordering:
0320-7177763
[email protected]

Soup industry

AAS
Transformed bacteria are used in enzymology for the production of enzymes. Moreover, the transformation is used to multiply copies of plasmids containing genes of our interest.
Contents of EBB Series-III
Experiment 1.1- Estimation of serum glucose (Ortho-toluidine Method) 6
Experiment 1.2- Estimation of serum fatty acids 7
Experiment 1.3- Estimation of serum triglyceride 9
Experiment 1.4- Estimation of serum cholesterol (Sulphuric acid method) 10
Experiment 1.5- Estimation of serum/tissue cholesterol, HDL and LDL/VLDL 11
Experiment 1.6- Estimation of glycerol (Enzymatic method) 13
Experiment 1.7- Estimation of phospholipids by non-destructive method 15
Experiment 1.8- Blood group determination 17
Experiment 1.9- Estimation of blood hemoglobin 17
Experiment 1.10- Estimation of serum ammonia (Nesseler’s and Salicylate Methods) 19
Experiment 1.11- Estimation of urea in blood and serum samples 22
Experiment 1.12- Estimation of serum creatinine kinase (Jaffe’s reaction) 23
Experiment 1.13- Estimation of serum lactic acid 24
Experiment 1.14- Estimation of serum uric acid (Uricase method) 26
Experiment 1.15- Estimation of total serum proteins by Lowry assay 27
Experiment 1.16- Estimation of serum albumin 29
Experiment 1.17- Estimation of serum bilirubin (Malloy and Evelyn) 30
Experiment 1.18- Estimation of serum ALT (SGPT) 31
Experiment 1.19- Estimation of serum AST (SGOT) 33
Experiment 1.20- Estimation of serum ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase) 34
Experiment 1.21- Estimation of serum TAC (Total Antioxidant Capacity) 34
Experiment 1.22- Estimation of serum TOS (Total Oxidant Status) 36
Experiment 1.23- Estimation of serum GSH (mg of GSH/g of protein) 38
Experiment 1.24- Estimation of serum catalase 40
Experiment 1.25- Estimation of tissue MDA (Malondialdehyde) 41
Experiment 1.26- Estimation of cytotoxicity through hemolytic activity 43
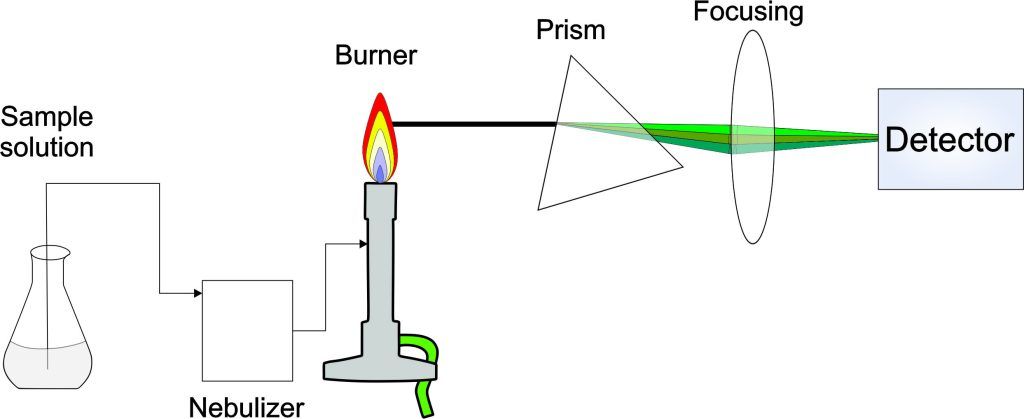
Experiment 1.27- Estimation of Na, K, and Ca (in serum and urine) by flame photometer 44
Experiment 1.28- Estimation of inorganic phorphorous (P) in serum and urine 46
Experiment 1.29- Estimation of chloride in a urine sample by titration 48
Experiment 2.1- Determination of moisture contents of raisin 51
Experiment 2.2- Determination of ash content of cabbage 52
Experiment 2.3- Estimation of fat contents in almond 53
Experiment 2.4- Estimation of fat by chloroform–methanol procedure (Folch extraction) 54
Experiment 2.5- Protein quantification by Kjeldahl method 55
Experiment 2.6- Estimation of vitamin C in orange samples (mg /g of fruit) 56
Experiment 2.7- Preparation of different extracts from fennel seeds 57
Experiment 2.8- Determination of total phenolic contents (TPCs) 58
Experiment 2.9- Determination of total flavonoids contents (TFCs) 60
Experiment 2.10- Determination of reducing power 62
Experiment 2.11- DPPH radical scavenging activity 64
Experiment 2.12- Hydrogen peroxide scavenging capacity (phenol and 4-aminoantipyrine) 65
Experiment 2.13- Antioxidant activity in linoleic acid system (inhibition of lipid peroxidation) 68
Experiment 2.14- Estimation of ABTS cation radical scavenging activity 69
Experiment 2.15- Estimation of hydroxyl radical scavenging activity 71
Experiment 2.16- Estimation of ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) 72
Experiment 2.17- Estimation of α-amylase inhibition assay 75
Experiment 2.18- Estimation of SOD (superoxide dismutase) activity 76
Experiment 2.19- Estimation of POD (peroxidase) activity 77
Experiment 2.20- Catalase activity (µM/mg of protein) 79
Experiment 2.21- Quantitation of citric acid 81
Experiment 2.22- Quantitation of succinic acid 82
Experiment 2.23- Antimicrobial activity of crude extract and standard drugs. 84
Experiment 2.24- Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) 85
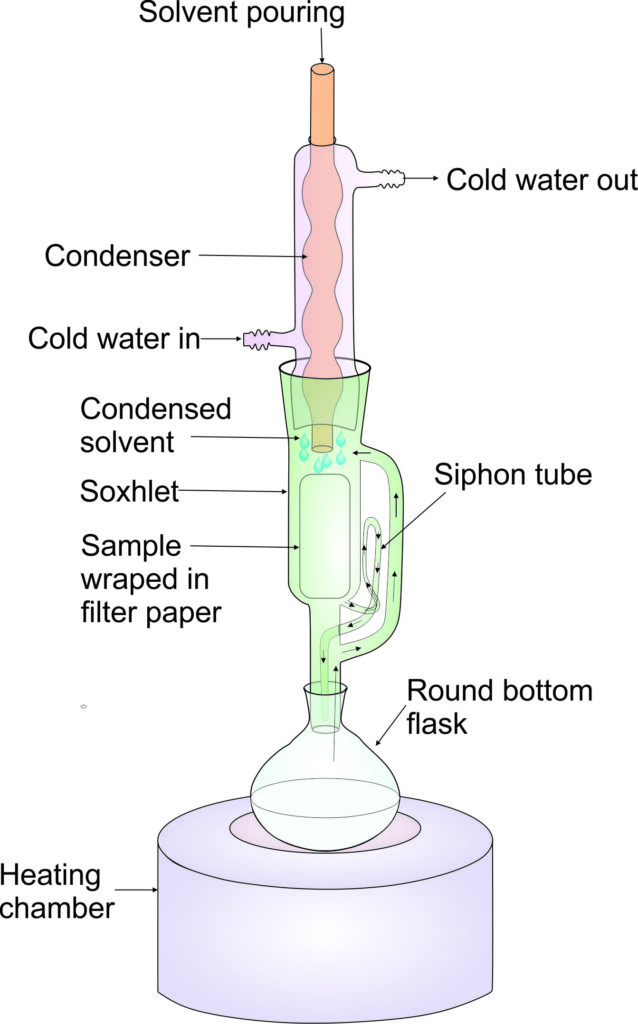
Experiment 3.1- Extraction of oil by Soxhlet method 88
Experiment 3.2- Determination of acid value 89
Experiment 3.3- Determination of iodine value (iodine monochloride) 89
Experiment 3.4- Determination of peroxide value 90
Experiment 3.5- Purification of phytochemicals by column chromatography 91
Experiment 3.6- Separation of phospholipids by TLC 91
Experiment 3.7- Determination of ethanol percentage in the fermentation broth 92
Experiment 3.9- Preservation of food by UV-radiation / chemical method 95
Experiment 3.11- Flow process diagram for sugar industry 95
Experiment 3.12- Flow process diagram for cooking oil industry 97
Experiment 3.13- Flow process diagram for fermentation and alcohol extraction industry 98
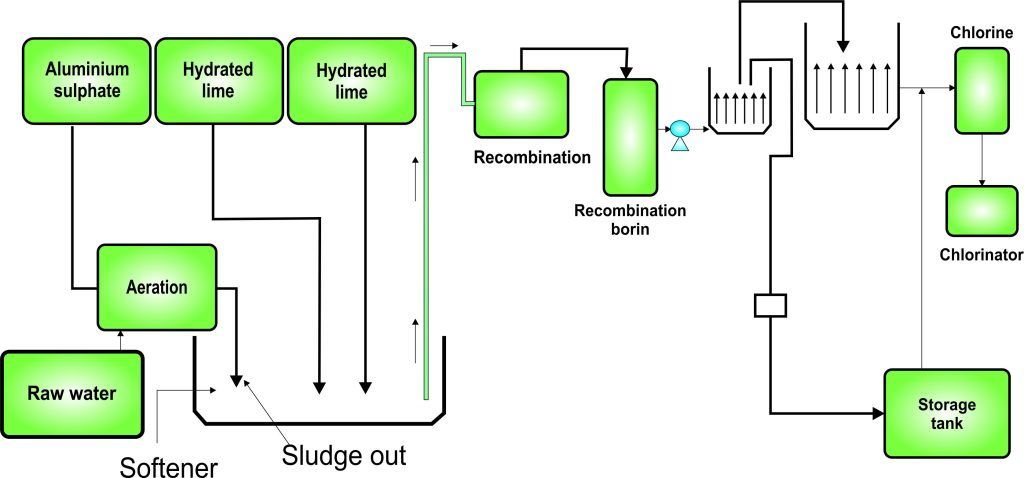
Experiment 3.13- Flow process diagram for waste-water treatment industry 98
Experiment 3.14- Flow process diagram for cloth industry 100
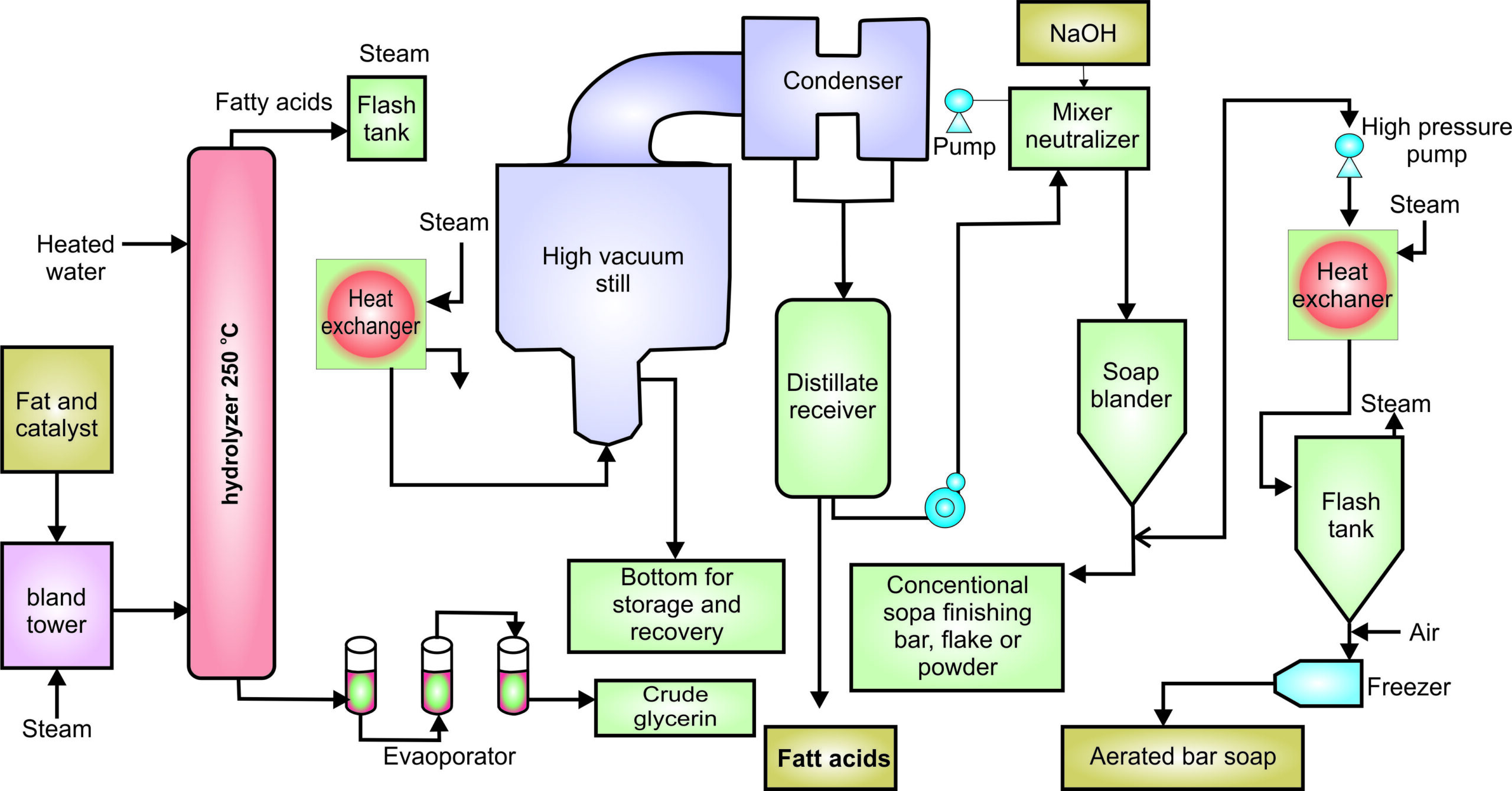
Experiment 3.15- Flow process diagram for soup industry 101
Experiment 4.1- Two-dimensional electrophoresis 103
Experiment 4.2- HPLC for the identification of specific phenolic compound 104
Experiment 4.3- LC-MS analysis of digested protein sample 105
Experiment 4.4- Flame photometry for the quantitation of alkali metals 106
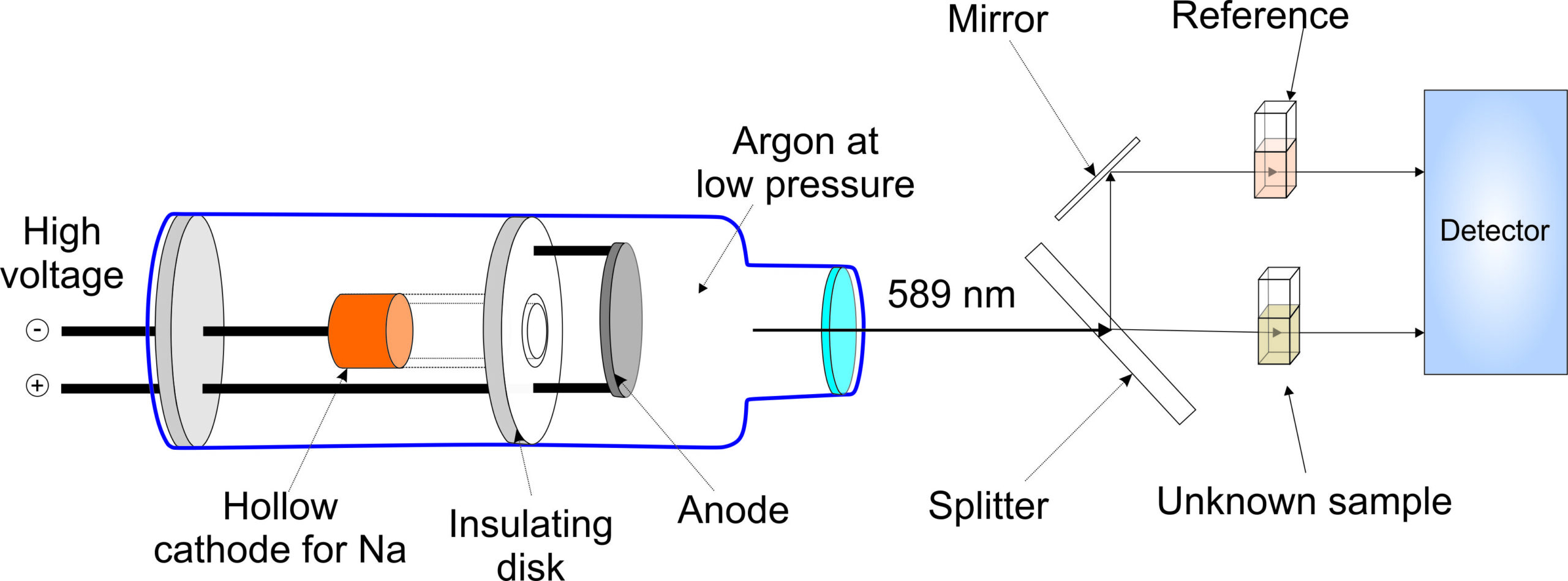
Experiment 4.5- Atomic absorption spectroscopy for the quantitation of metal ions 107
Experiment 4.6- Inductively coupled plasma for simultaneous quantitation of multiple elements. 107
Experiment 4.7- Circular dichromic analysis for protein structure determination 108
Experiment 4.8- FTIR study 109
Experiment 4.9- General methods of fractionation of DNA and proteins 110
Experiment 4.10- Dialysis of blood 111
Experiment 4.11- Lypholysation 112
Experiment 4.13- Fluorescence spectroscopy 112
Experiment 4.14- X-Ray crystallography 112
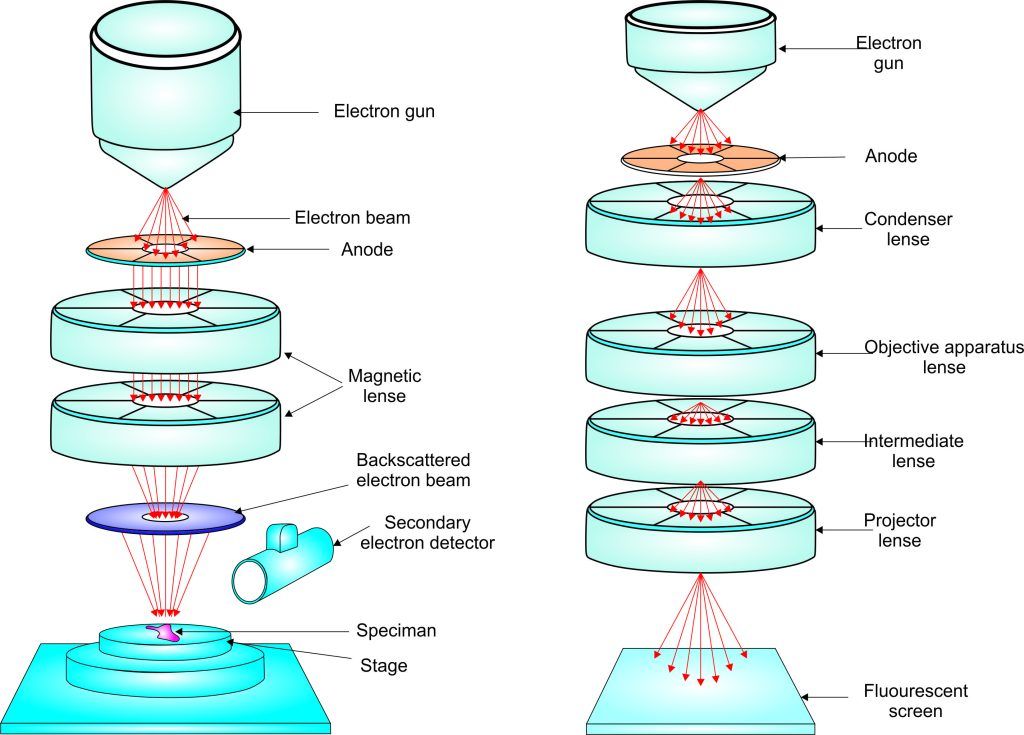
Experiment 4.15- Scanning tunneling microscope (TEM) 113
Experiment 4.16- Scanning electron microscope (SEM) 114
Experiment 4.17- Native SDS-PAGE 115
Experiment 5.1- Sterilization and germination of tomato sees 117
Experiment 5.2- Embryo culture, anther culture 117
Experiment 5.3- Micro culture for double haploid 117
Experiment 5.4- Micropropagation by auxiliary buds 118
Experiment 5.5- Adventitious shoot proliferation 118
Experiment 5.6- Plant regeneration by organesis 119
Experiment 5.7- Somatic embryo genesis from culture cells 119
Experiment 5.8- Meristem culture for virus elimination, 120
Experiment 5.9- Invitro fertilization 120
Experiment 5.10- Protoplast isolation and culture 121
Experiment 5.11- Agrobacterium mediated transformation 121
Experiment 5.12- ELISA to certify pathogen free plant 122
Experiment 5.13- Extraction and qualitative analysis of chlorophyll 122
Experiment 5.14- Extraction and qualitative analysis of starch 122
Experiment 5.15- Extraction and qualitative analysis of lipids 123
Experiment 5.16- Extraction and qualitative analysis of auxins 123
Experiment 5.17- Extractions and estimation of alkaloids, phenolics and flavonoids 124
Experiment 5.18- Oxygen estimation by Wiklers method 124
Experiment 5.19- Estimation of amylases from germinating seeds 125
Experiment 5.20- Determination of water potential by Chardakov’s method. 125
Experiment 5.21- Plant expression vectors 126
Experiment 5.22- Plant transformation 126
Exercise 6.1- Websites for searching articles and books 128
Exercise 6.2- How to search a research or review article? 128
Exercise 6.3- What is general anatomy (parts) of a research article or dissertation? 132
Exercise 6.4- Guidelines for the reading of a research article? 133
Exercise 6.5- How to write a research article? 134
Exercise 6.6- General guidelines for the font and page set-up for thesis (dissertation) 135
Exercise 6.7- Parts of ppt for the defence of research article, synopsis, or thesis defence 136
Exercise 6.8- How to select a topic of research? 136
Exercise 6.9- A list of funding agencies 137
Exercise 6.10- How to write a good application for funding? 137
Exercise 6.11- How to use Endnote to insert citation? 141
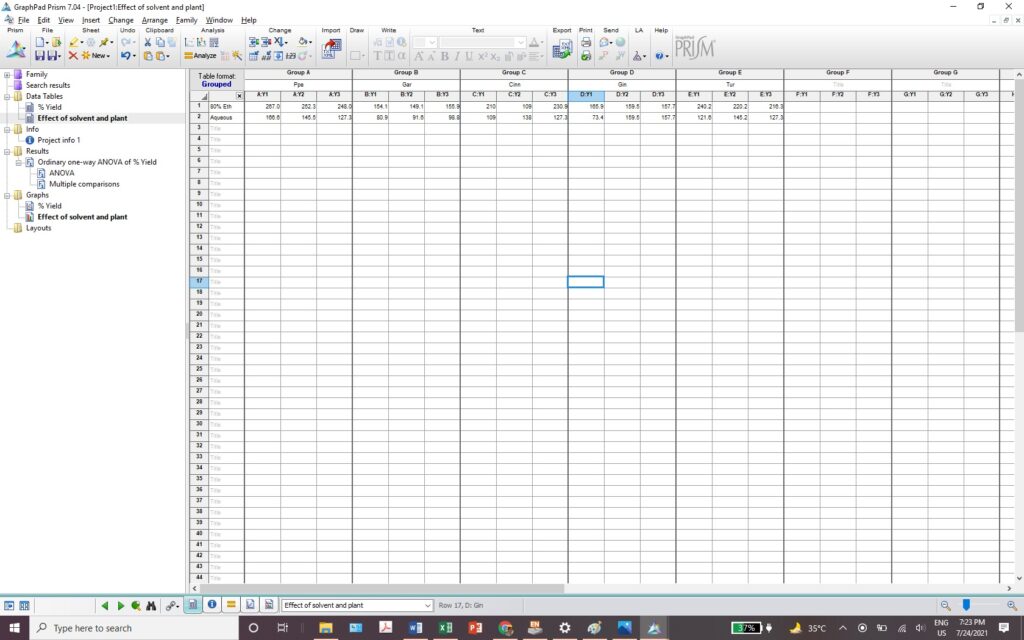
Exercise 6.12- How to use GraphPad Prism for One-way ANOVA? 146
Exercise 6.13- How to use GraphPad Prism forTwo-way ANOVA? 150
Exercise 6.14- How to use GraphPad Prism to find correlation? 153
7.1- Reagents for Biochemistry, Molecular & Cell Biology lab 156
7.3- Composition of reagents for making gradient SDS page gel (6-17 %) 160
7.4- Buffers composition for plasmid extraction 160
